by Allergy Partners
July 26, 2024
What Causes Hives? What You Need to Know About Urticaria
Experiencing hives for the first time can be nothing short of alarming. Fortunately, hives are generally not an indication of a serious illness, though they can be uncomfortable. Here’s what you need to know about the symptoms, causes, and treatment of hives.
Any sudden change in the skin’s appearance or texture can be highly worrying, and hives can appear very, very suddenly. In fact, hives can develop so quickly that it’s possible to watch the changes occurring in real-time!
What are hives?
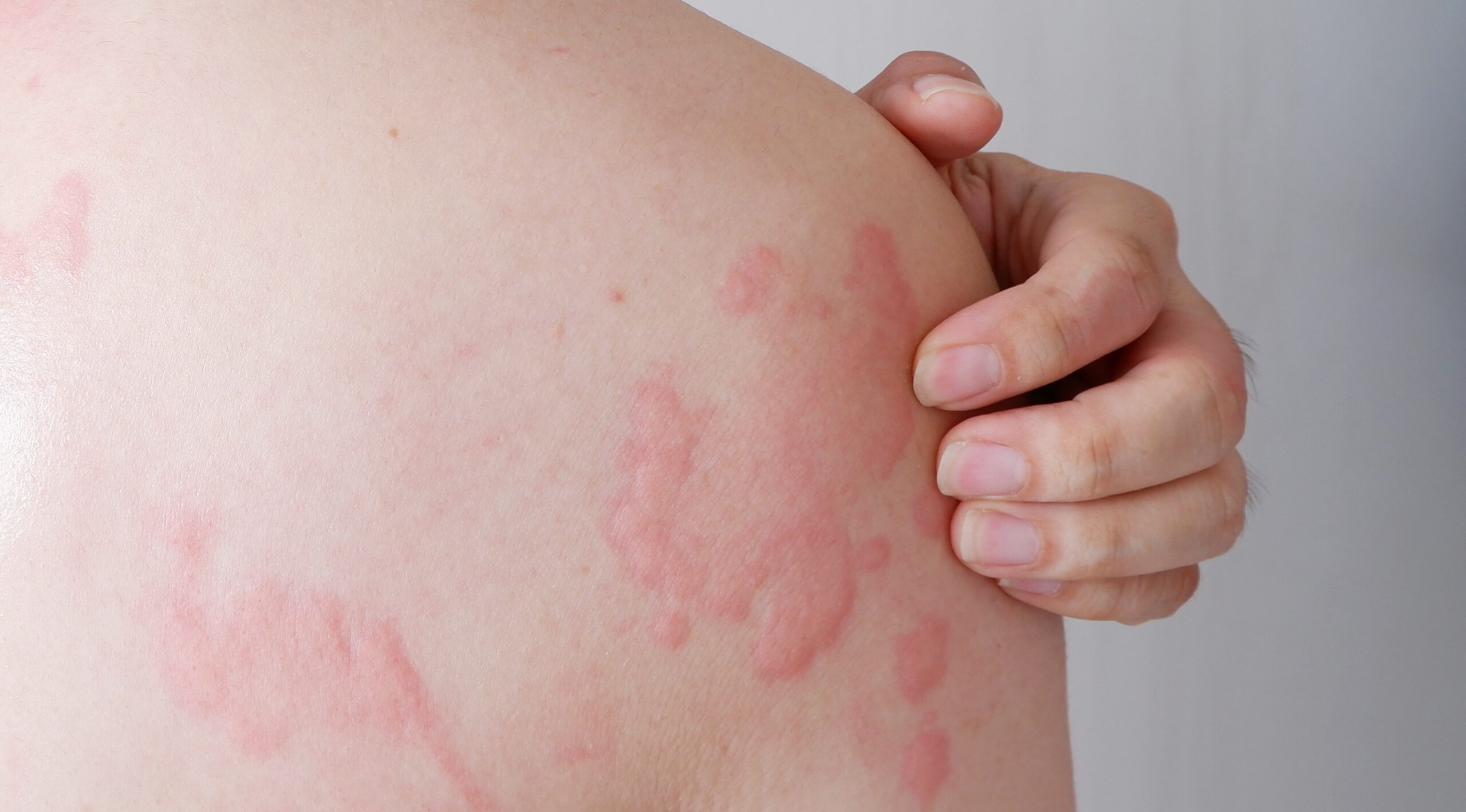
Hives, clinically known as urticaria or colloquially as wheals, are raised, splotchy skin eruptions that can be red, pink, or flesh-colored.
The size and severity of hives can vary greatly. They can range from small, itchy bumps that are less than 1/2 inch in diameter to large, swollen areas that can span several inches in diameter. In some cases, hives can be so extensive that they cover a significant portion of the body
What are the symptoms of hives?
The symptoms of hives can vary from person to person, but may include:
- Raised, red welts or bumps on the skin
- Itching, which may be severe
- Swelling and redness around the hives
- Burning or stinging sensation
Although hives may be uncomfortable and annoying, they are typically not a dangerous medical condition. However, in rare cases, hives can be a sign of a serious underlying disorder, such as an allergic reaction, infection, or chronic disease. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment is important.
Are hives a type of rash?
Yes, hives are a type of rash, but there are several noteworthy differences.
Not all rashes are hives. The majority of rashes heal slowly, taking 24 hours or longer to fade, potentially leaving scars and discoloration. Acute hives, on the other hand, typically resolve after a few hours and do not leave marks or scars.
Why do I have hives?
The exact cause of hives is not fully understood, but it is believed that an immune system reaction triggered by an allergen causes the release of histamine and other chemicals in the skin. This immune system overreaction can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to swelling and inflammation.
Hives can develop anywhere on the skin, including the face, arms, legs, and torso. They may also occur on the scalp, inside the mouth or throat, or around the eyes. The affected areas may be red, itchy, and swollen and may tingle or burn.
Did something I ate cause hives?
Hives can be caused by an allergen, which might come from various sources, including food, medications, or other potential irritants.
The cause of sudden urticaria can vary from person to person, but several potential factors can contribute to its development.
- Allergic Reactions: When the immune system mistakenly identifies a substance as harmful, it releases chemicals called histamines that cause the skin to become inflamed and itchy. Common triggers for allergic reactions include certain foods, medications, insect stings, latex, and certain medications.
- Infections: Viral infections, such as herpes simplex and shingles, can cause the body to release histamines, leading to the development of hives. Bacterial infections, such as strep throat and urinary tract infections, can also trigger hives as a symptom.
- Physical Factors: Exposure to heat, cold, pressure, or vibration can trigger an outbreak of hives. This can occur due to changes in body temperature, physical trauma to the skin, or certain physical activities.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In rare cases, hives can be a symptom of an underlying autoimmune disorder. Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, in this case, the skin. Conditions such as autoimmune hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have been shown to sometimes cause sudden urticaria.
- Stress and Anxiety: Although stress itself may not directly cause hives, it can play a role in triggering or exacerbating the condition. Emotional and physical stress can cause the release of stress hormones, which can increase inflammation and exacerbate allergic reactions.
Can water cause hives?
In very rare instances, exposure to water can cause an outbreak of hives.
Aquagenic urticaria is a rare disorder characterized by a sudden and severe outbreak of hives after coming into contact with water of any temperature. The water might come from natural sources, swimming pools, tap water, or even sweat. The condition affects an estimated .000001 of the global population.
The exact cause of aquagenic urticaria is not fully understood, but it is believed to be an immune response triggered by the proteins found in water.
Can clothing cause hives?
Physical urticaria is an outbreak of hives caused by an external, stimulating element. Restrictive clothing and belts can trigger hives.
Can the sun cause hives?
Solar urticaria is a rare condition where exposure to sunlight leads to an outbreak of hives. This condition is characterized by a rapid and severe reaction upon exposure to sunlight, resulting in itchy, red, and swollen skin.
The exact cause behind solar urticaria is not known, but it is believed to be related to an abnormal immune response triggered by sunlight.
Why won’t my hives go away?
The duration of an outbreak of hives depends upon whether the hives are chronic or acute.
Chronic Hives
Chronic hives symptoms are characterized by their persistence. These symptoms are similar to those of short-lived hives, but they occur at least twice per week and last for more than six weeks.
The exact cause of chronic hives is often difficult to determine. While there may be an underlying trigger in some cases, the majority of cases are considered idiopathic, meaning there is no known cause.
Acute Hives
Acute hives, also known as acute urticaria, are a temporary skin condition. The hives typically appear within minutes to hours and last for a relatively short duration, ranging from a few hours to a few days.
Acute hives can be triggered by a wide range of stimuli, such as certain foods, medications, environmental factors, viral infections, or exercise. However, not all triggers are known.
How are hives treated?
- Acute hives can be treated using the following interventions:
- Over-the-counter medications: Over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or loratadine (Claritin), can help block the release of histamine, a chemical in the body that triggers the allergic reaction that causes hives. These medications are usually safe when used as directed and can provide temporary relief.
- Prescription corticosteroids: In severe cases of acute hives, topical or oral corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and alleviate itch and discomfort.
- Cold compress: Applying a cold compress can provide temporary relief from acute hives by reducing swelling and itching.
- Colloidal oatmeal baths: Colloidal oatmeal baths can soothe the skin and reduce swelling associated with acute hives. The chemical structure of colloidal oatmeal reduces cytokines, a protein group that triggers an inflammatory response.
Chronic hives can be an indication of a more serious underlying medical condition. In some cases, they may be triggered by an undiagnosed infection or an underlying hormonal disorder, such as thyroid disease. Consulting a medical professional is crucial to rule out any potential underlying medical conditions that may be causing the hives.
In cases where the trigger responsible for the hives has been identified, your doctor will work with you to determine the best course of action.
Certain medications may be prescribed if the trigger for chronic hives is not known or if the patient’s immune system is responding abnormally. Antihistamines and H2 blockers are commonly used to treat chronic hives. They are typically prescribed orally and can be taken as needed.
While antihistamines and H2 blockers can provide temporary relief, they are not a long-term solution for chronic hives. Ongoing evaluation and management by a board-certified allergist are essential to ensure appropriate treatment and effectively address the condition.
Allergy Partners: Offering Effective Immunotherapy Solutions for Chronic Hives
At Allergy Partners, we specialize in providing a comprehensive range of services proven effective in managing and treating hives from allergies and other symptoms.
If you are struggling with hives or other allergy symptoms, contact the helpful team at Allergy Partners today to schedule a consultation.
